| Feature | Amazon Web Services | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Containers | Docker and Kubernetes | Kubernetes |
| Virtual machines | Yes | Yes |
| Load balancing services | Yes | Yes |
| Network service tiers | No | Yes |
| Distributed object storage | Yes | Yes |
| Geography-based routing | Yes | No |
| Free tier | Yes | Yes |
Pushing workloads to the cloud is one way businesses enhance scalability, flexibility and cost-efficiency while accessing advanced technologies and reducing the need for on-premises infrastructure. Here, we will compare two popular cloud services that help businesses migrate and manage their workloads in the cloud: Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud.
AWS provides businesses with the technical and operational capabilities to lift, move and manage workloads, including from Microsoft, SAP and VMware, and entire data centers to the AWS cloud ecosystem. By comparison, Google Cloud is a suite of cloud computing resources that offers businesses application migration, data migration and other cloud migration and management possibilities.
While AWS and Google Cloud offer efficient and quality cloud services, it’s necessary to evaluate the differences in pricing, security and compliance, and storage capabilities to ensure you choose the best tool for your business.
Jump to:
- Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud pricing
- Feature comparison: Amazon Web Services vs. Google Cloud
- AWS pros and cons
- Google Cloud pros and cons
- Choosing between Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud
- Review methodology
Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud pricing
AWS and Google Cloud have flexible and competitive pricing models, with some free perks to go with them. Businesses stand a chance of saving more with Google Cloud due to its per-second billing compared against AWS’s per-hour. Additionally, Google Cloud offers more discounts for customers who opt to use them long-term with no upfront cost.
PREMIUM: Check out the top three cloud platforms in this vendor spotlight.
However, it’s better to bear in mind that factors like data center location, level of workloads and networking requirements will influence the pricing, and there is not much difference between the two cloud platforms.
AWS pricing
AWS offers a pay-as-you-go pricing structure for the majority of its cloud services. This means customers can scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand, minimizing costs during periods of low usage. Other pricing options include:
- Save when you commit: Businesses are offered some discounts when they commit to use a certain amount of AWS services for longer periods of up to one to three years
- Pay less while using more: Discounts are offered to businesses as their usage volume increases.
Additionally, AWS offers a free tier with limited resources for new users to experiment and learn without incurring initial costs.
Google Cloud pricing
Google Cloud offers a pay-as-you-go pricing structure that allows users to pay for only the cloud services they use. Pricing varies by product and usage. Users can get started with their Google Cloud journey without committing to upfront fees or termination charges.
New customers can start by evaluating Google Cloud products with $300 in free credits and access to over 20 free products. Google Cloud also offers cost management tools that help users set budgets, quota limits and alerts.
Feature comparison: Amazon Web Services vs. Google Cloud
Security and compliance
AWS and Google Cloud deliver top security and compliance features for their customers. Regarding compliance, both platforms meet similar compliance standards, such as STAR, HIPAA, CSA GDPR and other ISO standards (Figure A).
Figure A
At the encryption level, the platforms provide their customers with encryption features for data in transit and at rest using 256-bit AES. Regarding firewalls, there is a slight difference in how both allow customers to manage and configure their cloud-hosted accounts and applications. AWS provides its firewall service as a different offering known as AWS Firewall Manager, while Google Cloud offers this service as part of its core Cloud Firewall service.
Network service tiers
Currently, Google Cloud is the only provider that offers network service tiers to its customers. Unlike AWS, customers are offered the opportunity to choose between the network service tiers, making it easy for users to optimize their networks based on price and performance (Figure B).
Figure B
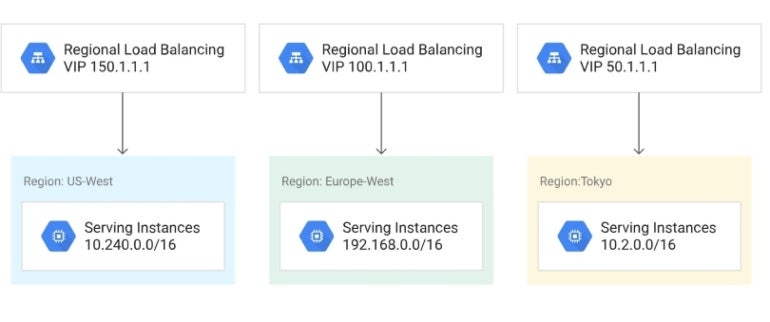
The two network service tiers available on Google Cloud are:
- Standard: A lower-performance network that does not include protection from a global service-level agreement.
- Premium: A high-performance and low-latency network and global network load balancing that offers protection from a global SLA.
File storage capabilities
Both platforms allow users to access file storage solutions that can help run cloud resources: Amazon Elastic File System and Google Filestore. With both services, customers have access to create, configure and store files using a fully managed file storage service while deployment, patching and maintenance infrastructure are managed by cloud providers.
SEE: For more information, check out our AWS cheat sheet.
Although both services offer similar file storage capabilities, some differences still arise. For instance, AWS’s EFS operates on version 4 of the Network File System Protocol, while Google’s Filestore runs its storage services on the older NFSv3.
Compute features
AWS offers a comprehensive suite of compute services to meet a wide range of cloud computing needs. At the core of its compute offerings is Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud, which provides secure and customizable virtual servers in the cloud. AWS’s compute portfolio also includes Amazon EC2 Spot for cost-effective fault-tolerant workloads, Amazon EC2 Autoscaling for automated capacity adjustments, and Amazon Lightsail for simplified application and website development.
On the other hand, Google Cloud’s compute feature, known as the Compute Engine, is a customizable compute service that enables users to create and run virtual machines on Google’s infrastructure (Figure C). It offers a range of virtual machine types tailored to specific workloads, including general-purpose, ultra-high memory, compute-intensive and accelerator-optimized machines, making it suitable for a wide array of applications and business requirements.
Figure C
AWS pros and cons
Pros of AWS
- Provides a vast array of cloud services and features, catering to diverse business needs.
- Has data centers in multiple regions worldwide.
- Offers a free tier for some of its services.
- Offers Auto Scaling, which automatically adjusts capacity for great performance.
Cons of AWS
- Pricing can be complex.
- Considered expensive compared to its competitors.
- Limited free tier.
Google Cloud pros and cons
Pros of Google Cloud
- Offers free cost management tools.
- Easy integration with other Google services.
- Google Cloud has a global network infrastructure.
- Good documentation, including a detailed API Reference guide.
Cons of Google Cloud
- Compared to AWS and Azure, Google Cloud has a smaller market share.
- Pricing can be complex, making it difficult for businesses to budget accurately.
Choosing between Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud
AWS and Google Cloud are both great platforms that offer a comprehensive suite of cloud services. However, picking one over the other should be subject to the unique requirements of your business.
If you are considering the price, remember that what you are billed depends on the services you include in your package. As a result, there are instances where AWS charges higher than Google Cloud and vice versa.
Furthermore, if you’re considering a platform that has been around for a longer time with wider reach, services and a great community, AWS might meet that need, as it’s been on the stage far longer than Google Cloud.
Review methodology
In comparing AWS and Google Cloud Platforms, we started by assessing each platform individually to understand their key offerings, pricing structure, global reach, support and documentation, integration and ecosystem. This helped us discover what they have in common and what separates them. We also considered user reviews to have an understanding of their usability ratings.


